

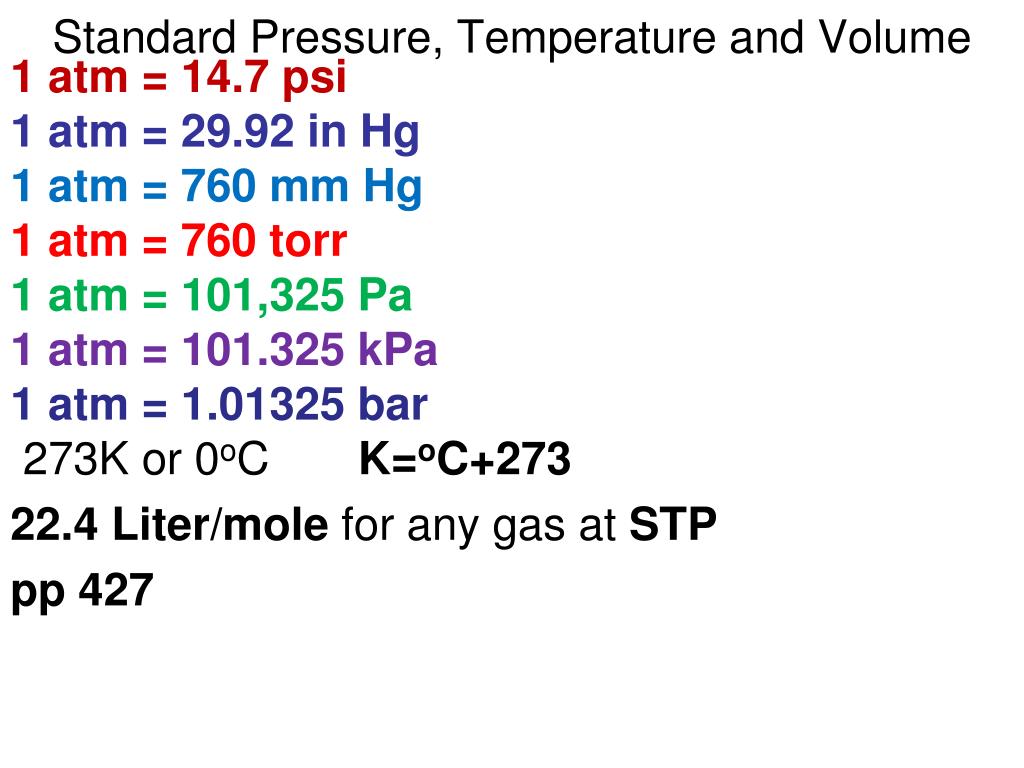
"atmosphere (atm, standard), atmosphere (technical), attobar, attopascal, bar, barad, barye, centimeter of mercury (0☌), centimeter of water (4☌), centibar, centipascal, centipascal, centitorr, decibar,ĭecipascal, dekabar, dekapascal, dyne/square centimeter, exabar, exapascal, femtobar, femtopascal, foot of air, foot of mercury, foot of water, gigabar, However, other units like inches of mercury (inHg) and pounds per square foot (psf) are also used in specialized fields. In the Imperial system, the most popular pressure unit is the Pound per Square Inch (psi). However, the Bar (bar) is also commonly used for expressing pressure in Metric applications. In the Metric system, the Pascal (Pa) is the primary unit for pressure.
Millimeter of Mercury (mmHg): Often used in medical settings for blood pressure measurements. Atmosphere (atm): A unit used to express atmospheric pressure, especially in weather reports.ĥ. Pound per Square Inch (psi): Commonly used in the United States for measuring pressure in various industries.Ĥ. Bar (bar): Widely used in meteorology, industrial processes, and fluid dynamics.ģ. Pascal (Pa): The SI unit of pressure, commonly used in scientific and engineering applications.Ģ. The converter will instantly displays the converted pressure value, rounded to four decimal places by default.ġ. Select the target pressure unit you wish to convert to.Ħ. Select the initial pressure unit you wish to convert from.Ĥ. By default, the converter is set to round the results to four decimal places.ģ. Select the desired accuracy level from the provided drop-down list.
Tire pressure conversion kpa to psi how to#
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use the pressure converter:Ģ. If you require greater precision, you can manually adjust the number of decimal places up to 10. By default, the pressure converter rounds the result to 4 decimal places for clarity and convenience. The pressure unit converter provides quick and accurate conversions, making it a valuable tool for engineers, scientists, meteorologists and anyone dealing with pressure measurements. Although the Pascal is used more in the scientific context, PSI is used more day-to-day. From tire pressure to gas pressure and quite a few others. The system came into use in England about 1300 and was used primarily in the international wool trade.Ĭurrent Use: PSI is used worldwide to measure a lot of pressures. It is based on the avoirdupois system, a system that uses weights in terms of the avoirdupois pound, which was standardized in 1959. History : This unit finds its history in the imperial and American system of units of measure. One PSI is approximately 6.895 Pascal (N/m2). It is defined as the pressure created when a force of one pound-force is applied to a surface of one square inch. To be able to do this anyway, an average approximation is always used.ĭefinition : A PSI is a unit used worldwide. Because it is not the same everywhere, you cannot simply apply a conversion factor to convert PSI to Pa or bar. The pressure that a Pound delivers depends on gravity which is not the same everywhere on earth. The PSI is an American unit and stands for Pounds per Square Inch. 1 atmosphere is therefore 1013 millibars and 1013 hectopascals. In this case, 1 millibar is exactly equal to 1 hectopascal. Air pressure is also regularly expressed in millibars or hectopascals. The atmosphere corresponds more closely to the average air pressure at sea level, and is defined as follows: 1 atm = 101.325 Pa so just over 1 bar.

Meteorologists and weather forecasters worldwide use this unit, as an expression in Pascal would lead to much longer numerical results. Where atmospheric pressure equals 1013.25 mbar (101.325 kPa). Millibars (symbol: MB) is also commonly used to describe atmospheric pressure.
Tire pressure conversion kpa to psi free#
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures, while indicating that authors are free to use bar, has not included it in the permitted list of the SI. The term “bar” comes from the Greek word “baros,” meaning weight.Ĭurrent usage : Although bar is the unit of pressure, it is not accepted by the International System of Units (SI) and is even disapproved in some areas. History: Bar was once introduced by Vilhelm Bjerknes, a Norwegian meteorologist who was at the forefront of modern weather forecasting. This unit is pretty much the standard reference when it comes to pressure. The bar is defined as 100,000 Pa, or 100 kPa.

The bar is originally a British unit, and 1 bar roughly corresponds to the average air pressure at sea level (although 1 atmosphere (atm) is a better description). However, Pascal is not the only unit used for pressure:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
